Founded: 1955
Founder: Genichi Kawakami
Headquarters: Iwata, Shizuoka, Japan
Official website: www.global.yamaha-motor.com
Yamaha Motor is one of the world’s largest and best-known manufacturer of motorcycles, ATVs, snowmobiles, and boats. The company was established in 1955 in Japan, as a sub-brand of the famous group, founded at the end of the 19th century, Nippon Gakki, which eventually changed its name to the last name of the founder of the empire — Torakusu Yamaha.
Motorcycle History
The Nippon Gakki management debated what postwar Japan needed most. Among the options were sewing machines, scooters, and primitive three-wheelers. In the end, they settled on motorcycles because the company’s equipment was suitable for it. A German DKW motorcycle was chosen as the prototype.
Less than 10 months later the first Yamaha motorcycle, the 125 CC YA-1, was completed. Yamaha admitted that it borrowed several features from DKW, including the four-speed transmission.
1956 was a successful year for the company. In addition to the high-profile sporting achievements, the product line was expanded. An improved model Ya-2 was launched, equipped with a 6.8 hp motor. Another debut of the 1950s was the YC1 motorcycle with a 175 CC two-stroke single-cylinder engine rated at 20 hp.
But already in 1957, luck turns away from Yamaha Motor. The new model YD-1 has a long list of flaws and vulnerabilities. The company is flooded with a huge number of complaints.
Yamaha decides not to stop and in 1959 the company manufactured YDS-1, a five-speed gearbox, twin-tube frame, two carburetors, and a 22 hp engine.
Where are Yamaha motorcycles made?
The main production plant of the company is located in Japan, though Yamaha has facilities all over the world, mainly in Asia.
The 1960s were really rich years for YAMAHA Motor: business was booming in all areas. Only in 1960, the company produces 138 thousand motorcycles, which exceeds the previous figure by 600% (!). The company was actively conquering foreign markets (the recession in the domestic economy was pushing it, among other things). Thus, 12 thousand bikes were exported in 1962, and two years later – 87 thousand.
The 1960s were also marked by technical innovations. Engineers invented the Autolube technology, which translates as “auto-grease”. It helped improve two-stroke engines by dispensing oil to the cylinders and bearings. Autolube made it possible to create a new class of sports motorcycles.
The model range is expanding. In 1966, the YDS-3 makes its premiere. This road bike was the first, which has won great popularity among the American public – especially for its low weight and ease of operation.
In 1967, the model Yamaha TD1C 250 saw the light. This motorcycle racing class for a few years won almost all of its competitors with four-stroke engines.
But the real breakthrough was the 1968 premiere – the DT-1 model. This bike became the founder of a whole class enduro, which was dynamically gaining popularity in those years. The motorcycle was equipped with a 250 cm³ single-cylinder two-stroke engine, which was capable of producing 18 hp. The high ground clearance, low weight, and soft suspension made off-road riding a pleasant adventure.
In 1970, Yamaha Motor produced more than half a million motorcycles and released another iconic model. The brand’s first motorcycle is equipped with a four-stroke engine, the XS-1. At that time, the XS was not yet associated with a miniature clothing size: this model is large, full-size, luxurious, with a 650 CC engine.
Even more economical was the Passol scooter, with a two-stroke single-cylinder 49 CC engine. The scooter could reach speeds up to 35 km/h and weighed only 45 kg.
In 1973, the range of the company was expanded with the Yamaha RD350. It was equipped with an in-line air-cooled two-cylinder engine, capable of producing 35 hp and reaching a speed of 149 km/h. Fans of the brand affectionately called the model “pocket rocket” and sincerely loved it for its low cost, lightness, simplicity, and reliability.
In 1978, another big premiere came out: the XS1100 was the first bike with a 95 hp air-cooled inline four-cylinder engine and a propeller shaft. The end of the 1970s was marked by high-profile sports victories: in addition to the already mentioned triumph in the rally, the team’s riders have won the world championship of circuit racing three times since 1978.
In 1980, the legendary Virago 750 road bike was put into production. It was the first bike with a twin-cylinder air-cooled V-engine in the company’s lineup. The model with partial modifications rolled off the assembly lines for 17 years.
The next successful innovation of the brand was the FZ750, which saw the light in 1985. It was the first in the world! – was equipped with a five-valve engine with two camshafts.
In 1997, the YZ400F saw the light, which made the company a world motocross champion again. In 1998, the YXF-R1 debuted – a sportbike with a weight of only 177 kg, a four-cylinder 998 CC engine, and 150 hp.
Who owns Yamaha?
Yamaha Motor is owned by Yamaha Corporation, but Toyota also has a small stack in the company.
In 2006, the flagship product line became the YZF-R6 model. It was the first motorcycle with the YCC-T system: an electronically controlled throttle helped achieve the maximum acceleration. In 2007, the sports flagship YZF-R1 received a smart throttle system. Besides, it was replaced by a slipping clutch.
In 2011, the company produces its first touring enduro XT1200Z Super Tenere, challenging competitors – especially BMW. The designers have applied the most advanced technologies in the novelty.
2013 was the premiere year for the MT-09 motorcycle. This bike was equipped with an inline three-cylinder motor with a displacement of 847 CC and a power of 115 hp. According to the designers, it represents the best ratio of weight, power, and torque.
In 2017, the MT-09 was redesigned and improved. As part of the restyling, it got a new exhaust system, a slip clutch, a quick shifter, and a stiffer rear suspension.
The loudest new product of 2018 was unveiled at the 2018 Milan show. The NIKEN GT Sport Tourer tricycle with two wheels on the front axle promises an unprecedented level of comfort and safety.
As of today, the brand is second only to its age-old rival, the Honda brand, in terms of production volumes. The factory facilities of YAMAHA Motor are located in 45 countries around the world, more than 100 thousand people are employed at the enterprises.
Brand Logo
1955 – 1964
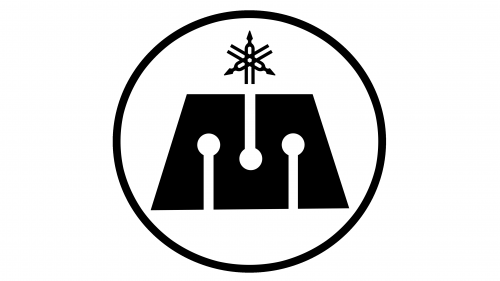
The logo of the company consists of two elements. One of them is a solid black trapezoid shape with three white knobbed batons drawn over it. The other symbol looks like a stylized star above it. In fact, it is three tuning forks crossed to create a proportioned pattern. It was meant to symbolize technology, sales, and production, which are considered to be the three pillars of Yamaha’s business. This symbol became closely linked to the brand.
1964 – now
A round emblem with three crossed tuning forks, which were seen in earlier logos, was introduced in 1964. The round emblem stands for unity as well as the spread of Yamaha’s influence across the globe. It is accompanied by the company name printed using all uppercase letters and a bold, sans-serif font that resembles Jay Gothic URW T Extra Bold font. The black and white color palette as well as the simple, clean design of the logo allowed the company to use it for several decades and across all its products without making any modifications.
1998 – now
The visual identity of Yamaha Motor fully repeats the iconic Yamaha logo, used on all the products of the huge iconic brand. The circular emblem with an elegant and edgy white image in the middle is accompanied by a bold and slightly narrowed logotype in the uppercase, which is usually placed under the badge.
Yamaha R1 Logo
The only Yamaha bike, which uses a separate logo is R1. This sporty model is known for its top-notch technical characteristics and speed, and the sharp red logo of the motorcycle brilliantly reflects it. The logo of Yamaha R1 is composed of a stylized inscription, which is usually executed in black or red. The letter and number of the model’s name are italicized and have their angles sharpened and some lines slightly elongated. The R1 badge evokes a sense of strength and determination, along with speed and power.
Emblem and Symbol
The Yamaha emblem is one of the most well-known badges all over the globe. This elegant image with an obvious Asian touch is not just a design, but has a meaning, pointing to its legacy and first years of the company:
The Yamaha logo appeared only in 1927, and today it is used by both the parent Yamaha Corporation and its subsidiary Yamaha Motor Company. It represents three tuning forks in a circle. The difference is that Yamaha Corporation has the tuning forks inscribed in a circle, while Yamaha Motor Company has the tuning forks crossing the circle.
The mark symbolizes the 3 main aspects of the company’s development – technology, production, and sales. Also, the symbol was originally interpreted as follows: “Let us represent on the world stage a strong alliance: “Production + technology + marketing”. Today there is also another meaning of each of the 3 tuning forks: “Customer”, “Society” and “Person”.
Font and Color
The clean and stable Yamaha logotype in all capitals is executed in a traditional and straight sans-serif typeface with bold lines and square cuts of the ends. The fort of the Yamaha visual identity is very similar to Trade Gothic Display, and also has a resemblance with Born Strong Black.
As for the color palette, the Yamaha Motor emblem most often uses a red and silver of white combo, which looks bright and fresh and evokes a sense of determination, power, and passion.
The Legends
Yamaha has released many models, which have become legendary, but 1975 was the year, which game most of them, it was a rich year for premieres. The XS360 had a two-cylinder 358 CC engine with 34 horsepower and a six-speed transmission. The XS250 also saw the light in 1975, with a 250 CC engine rated at 27 hp.
But the most promising development was the enduro XT500. It was equipped with a single-cylinder four-stroke engine 499 CC and 30 hp. Speed of 140 km/ h was quite decent for riding on the tracks, and the design – lightweight, narrow, with plenty of ground clearance – allowed to race and off-road, which made it a dual-purpose bike.